Liver transplantation is a medical procedure that can save the lives of individuals suffering from end-stage liver disease or acute liver failure. It has revolutionized the treatment of such conditions and offers a renewed lease on life for those whose liver function has severely deteriorated. This article will discuss who may require a liver transplant, the procedure’s safety, what preparation is necessary for surgery, and the criteria used to select eligible candidates. We will also explore those who may not be suitable for this complex medical intervention. Most liver transplants are performed to treat chronic liver diseases that have caused irreversible damage to the liver. Some of the common conditions that may require a liver transplant include cirrhosis, liver cancer, hepatitis B or C, autoimmune liver diseases, and genetic liver diseases.
Who Needs a Liver Transplant?
A liver transplant is a crucial procedure that can save a person’s life when their liver is severely damaged and can no longer function properly. It is usually recommended when other medical treatments and therapies have failed to improve the patient’s condition.
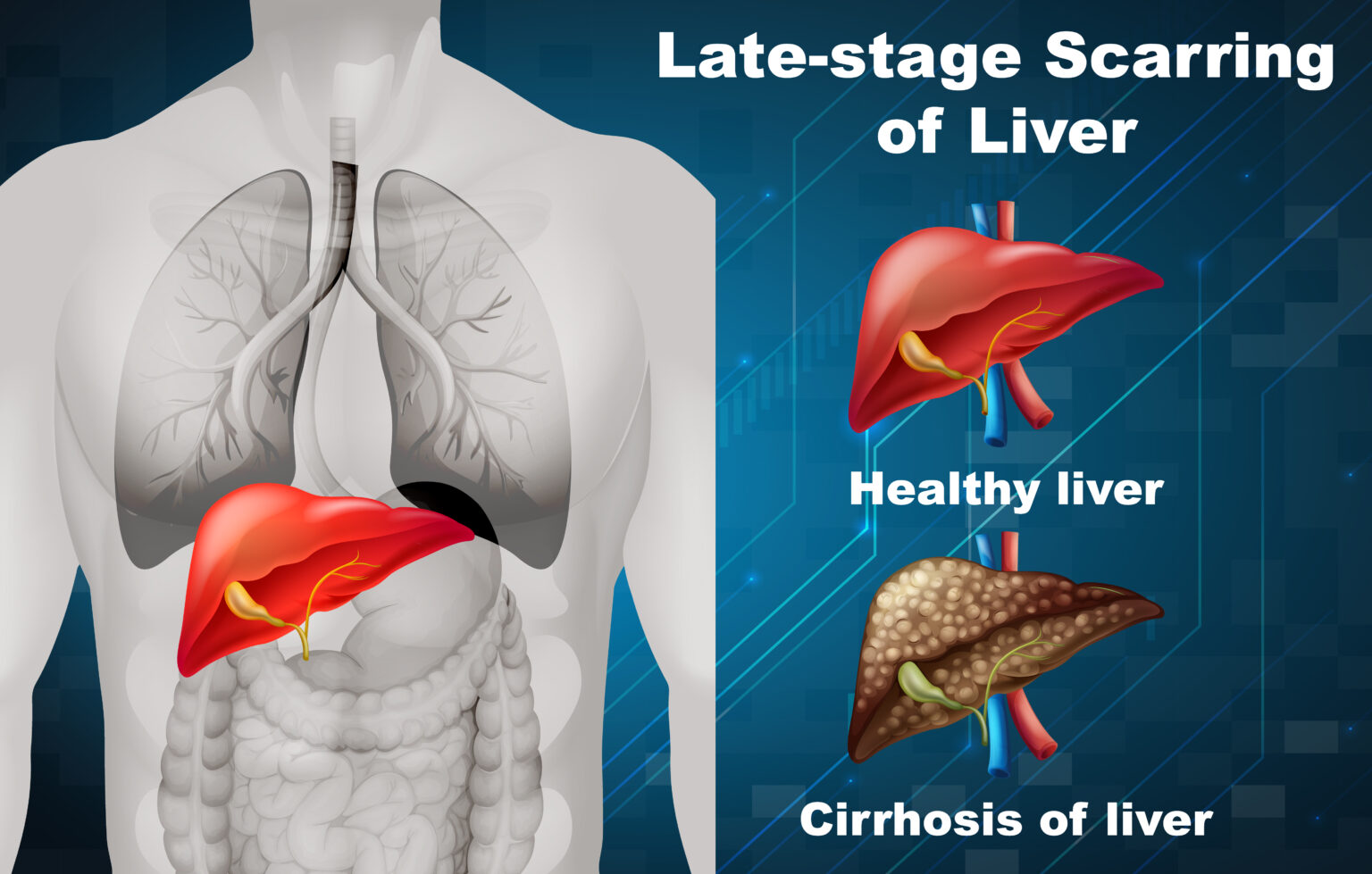
End-stage liver disease refers to long-term conditions such as cirrhosis, hepatitis B or C, alcoholic liver disease, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which can cause progressive damage to the liver over time. This can eventually lead to a point where the organ cannot perform its vital functions.
Acute liver failure, on the other hand, is a sudden and severe form of liver dysfunction that viral infections, drug-induced injury, or other acute conditions can cause. In such cases, an urgent liver transplant may be necessary to save the person’s life.
The Safety of the Procedure
Liver transplantation in India is an extremely complex and advanced surgical procedure. Thanks to medical advancements, it is possible to prolong the lives of patients suffering from liver diseases without compromising their quality of life. Improvements in surgical techniques, immunosuppressive medications, and post-operative care have significantly increased liver transplants’ safety and success rates. However, as with any major surgery, there are potential risks, such as bleeding, infection, organ rejection, and complications from anesthesia. The safety of the procedure is dependent on the patient’s health, the expertise of the transplant center, and meticulous post-operative care.
How do you prepare for liver transplant surgery?
Preparing for a liver transplant involves a thorough assessment and careful planning. The process includes several steps:
- Medical Evaluation: The patients undergo extensive medical testing to determine the severity of their liver disease, assess their overall health, and rule out any contraindications.
- Psychosocial Evaluation: A thorough assessment of the candidate’s mental and emotional well-being is performed to ensure they can cope with the procedure’s demands and the post-transplant lifestyle.
- Finding a Suitable Donor: It is crucial to have a suitable donor, either living or deceased. Living donors are evaluated for compatibility and overall health.
- Immunosuppressive Medications: Candidates must understand the importance of adhering to lifelong medication regimens to prevent organ rejection.
Who Is Suitable For Liver Transplantation?
Liver transplantation is not suitable for everyone with liver disease, as certain criteria must be met to be considered for the procedure. Some of the factors that determine eligibility are as follows:
Severity of Liver Disease: Candidates with severe liver damage or acute liver failure that does not respond to medical treatment are considered for transplantation.
Age and Overall Health: Younger individuals with good overall health and without significant health issues are often prioritized for transplantation.
Compliance: Candidates must demonstrate their willingness and ability to adhere to post-transplant care, including medication regimens and follow-up appointments.
Who Cannot Undergo Liver Transplantation?
Liver transplantation is a medical achievement that can be life-saving, but there are circumstances where it may not be possible or advisable. Some of these include:
Advanced Age: Older patients may not be suitable candidates for liver transplantation as the risks associated with surgery and post-operative recovery may outweigh the potential benefits.
Advanced Cancers: Extensive cancer that has spread beyond the liver or is deemed untreatable may exclude a candidate from transplantation.
Other Chronic Conditions: Medical conditions such as uncontrolled infections, severe heart or lung disease, HIV infection, brain dysfunction, or other issues that may hinder recovery might preclude transplantation.